Mauritius: Mauritius Communication Profile
2013/08/18

The island country of Mauritius benefits from an advanced and innovative telecom sector. It was the initial market in the better Africa region to launch cellular systems (in 1989), the initial to provide commercial 3G mobile service (2004), the initial in the world to develop a nationwide WiMAX wireless broadband network (2005), and one of the initial to launch IPTV services (2006). 4G services based on LTE have as well been launched, providing data at up to 100Mb/s.
With strong tourism and financial services sectors, Mauritius’s economy is expected to continue growing at additional than 4% per year.
The incumbent telco, Mauritius Telecom has been partially privatised and presently benefits from the scale and technical prowess of France Telecom/Orange, which holds a 40% interest in the operator. All sectors of the market are open to competition. Served by a modern, digital fixed-line network, fibre optic submarine cables for international connectivity, three mobile networks, a number of broadband and other service providers, Mauritius is successfully pursuing a policy to make telecommunications the fifth pillar of its economy and to become a regional telecom hub with Singapore as a role model. The government has been active in promoting its national broadband policy, and as well been instrumental in securing infrastructure upgrades, inclunding an upgrade for satellite connectivity to Rodrigues, which became operational in mid-2013.
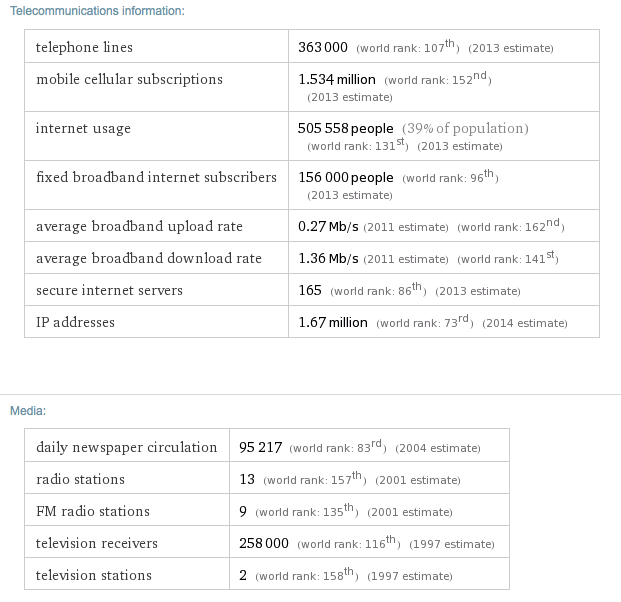
The mobile market, with penetration at 122%, is migrating from voice to data services. There are three GSM networks – Orange (Mauritius Telecom in partnership with France Telecom/Orange), Emtel (operated by Millicom International) and Mahanagar, a subsidiary of India’s MTNL which is as well the island\'s second fixed-line operator using CDMA2000 technology.
The highest increase rates are currently seen in the mobile broadband sector, where HSPA and EV-DO based 3G services are competing with fixed-line DSL and other wireless broadband offerings, inclunding WiMAX. FttC and FttP rollouts are in evolution and have by presently brought 100Mb/s connections to businesses, with nearly nationwide coverage planned for 2015. The landing of a second international submarine fibre optic cable has brought prices down further in a broadband market that was by presently one of Africa’s most developed.
Market highlights:
Bharat Telecom launched phase two of its fibre broadband project; Mauritius Telecom reports fall in revenue for 2013 but continues investment in national fibre network; Millicom sells its stake in Emtel to Currimjee Jeewanjee; Mauritius Telecom aims to expand the reach of its FttP network to 50,000 households by the end of 2014, with FttP delivering 30Mb/s services to 60% of households by 2015, scaling up to 100Mb/s nationally by 2020 as part of the National Broadband Policy 2012-2020; telecom sector’s share of in general ICT revenue continues to fall; regulator reduces price international private leased circuits by 16%, effective from early 2014; regulator sets up an internet service capped at Rs200 per month to encourage connectivity, subsidised by the Universal Service Fund; statement includes telco\'s operating data to Q1 2014, regulator’s, market data to December 2013, recent market developments. Estimated market penetration rates in Mauritius’s telecoms sector – end-2013
| Market | Penetration rate |
|---|---|
| Mobile | 121% |
| Fixed | 26% |
| Internet | 47% |
(Source: BuddeComm based on various sources)
.mu
- Mauritius News
-
- AFGHANISTAN: UNWTO: International tourism – strongest half-year results since 2010
- BOTSWANA: Why governments need to support the financial sector to meet the unserved needs of smallholder farmers
- BOTSWANA: International Arrivals To Africa Reach More Than 18 Million In 2017
- BOTSWANA: Africa: USA-Africa - No Policy? Bad Policy? or Both?
- BOTSWANA: Africa: U.S. State Department To Get Experienced Diplomat in Key Africa Post
- BOTSWANA: Africa’s economic growth in 2016 was driven by East Africa
- Trending Articles
-
- CAMEROON: Cameroon: Giving Priority to Education
- CAMEROON: Cameroon: English-speaking Students Do Not Return to School
- RWANDA: Rwanda: RDB's Good Problem - More Gorillas, Less Habitat
- ANGOLA: Angola's Elections Trigger a Crisis of Legitimacy
- BURUNDI: Burundi: Govt Rejects UN Accusations of Crimes Against Humanity
- RWANDA: Rwanda: Medical Drone Delivery System Wins Prestigious Global Award






