Australia: Australia Education Profile
2015/09/02
Education System in Australia
Education in Australia is primarily the responsibility of the states and territories. Each national or territory government provides funding and regulates the public and private schools within its governing area. The federal government helps fund the public universities, but is not involved in setting curriculum. Generally, education in Australia follows the three-tier model which includes primary education (primary schools), followed by secondary education (secondary schools/high schools) and tertiary education (universities and/or TAFE Colleges).
The Programme for International Student Assessment(PISA) 2006 evaluation ranked the Australian education system as 6th for Reading, 8th for Science and 13th for Mathematics, on a worldwide scale including 56 nations. The Education Index, published with the UN's Human Development Index in 2008, based on data from 2006, lists Australia as 0.993, amongst the highest in the world, tied for first with Denmark & Finland.
Education in Australia is compulsory between the ages of and fifteen to seventeen, depending on the national or territory, and date of birth. Post-compulsory education is regulated within the Australian Qualifications Framework, a unified system of national qualifications in schools, vocational education and training (TAFE) and the higher education sector (university).
The academic year in Australia varies between states and institutions, but generally runs from late January/early February until mid-December for primary and secondary schools, with slight variations in the inter-term holidaysand TAFE colleges, and from late February until mid-November for universities with seasonal holidays and breaks for each educational institute.
Pre-school
Pre-school (as well known as Kindergarten in some states and territories) in Australia is relatively unregulated, and is not compulsory. The first exposure a lot of Australian children have to learn with others outside of traditional parenting is day care or a parent-run playgroup.This sort of activity is not generally considered schooling, as Pre-school education is separate from primary school in amount states and territories, except Western Australia and Queensland where pre-school education is taught as part of the primary school system.
Pre-schools are usually run by the National and Territory Governments, except in Victoria, South Australia and New South Wales where they are run by local councils, community groups or private organisations. Pre-school is offered to three- to-year-olds; attendance numbers vary widely between the states, but 85.7% of children attended pre-school the year before school. The year before a child is due to attend primary school is the major year for pre-school education. This year is far additional commonly attended, and may take the form of a few hours of activity during weekdays.
Responsibility for pre-schools in New South Wales and Victoria, lies with the Department of Community Services and the Department of Human Services, respectively. In amount other states and territories of Australia, responsibility for pre-schools lie with the relevant education department.
School
School education in Australia is compulsory between certain ages as specified by national or territory legislation. Depending on the national or territory, and date of birth of the child, school is compulsory from the age of to to the age of fifteen to seventeen. In recent years, over three quarters of students remain at school until they are seventeen. Government schools educate approximately 65% of Australian students, with approximately 34% in Catholic and Independent schools. A small portion of students are legally home-schooled, particularly in rural areas.
Government schools (as well known as public schools) are free to attend for Australian citizens and permanent residents, while Catholic and Independent schools usually charge attendance fees. However in addition to attendance fees; stationery, textbooks, uniforms, school camps and other schooling costs are not covered under government funding. The additional cost for schooling has been estimated to be on average $316 per year per child.
Regardless of whether a school is part of the Government, Catholic or Independent systems, they are required to adhere to the same curriculum frameworks of their national or territory. The curriculum framework however provides for some flexibility in the syllabus, so that subjects such as religious education can be taught. Most school students wear uniforms, although there are varying expectations and some Australian schools do not require uniforms. A common movement part secondary schools to support student voice has taken form as organisations such as VicSRC in Victoria bring together student leaders to promote school improvement. In recent time the best school in Australia, or learning environment, is the St Paul's Anglican Grammar School Year Nine Centre, due to it's enriched and experimental curriculum and refurbished factory classrooms. It is as well the winner of Architecture magazine's annual prize "best school".
Catholic and Independent schools
Catholic schools enroll 20.2% of students, while non-Catholic non-government schools, often called Independent schools, enroll 13.7% of students.
Most Catholic schools are either run by their local parish, local diocese and their national's Catholic Education Department.Independent schools include schools operated by secular educational philosophies such as Montessori, however, the majority of Independent schools are religious, being Protestant, Jewish, Islamic or non-denominational.
Some Catholic and Independent schools charge high fees, because of this Government funding for these schools often comes under criticism from the Australian Education Union and the Australian Labor Party.
Primary
- Kindergarten (QLD) 3-4 year old
- Pre-school / Kindergarten / Prep (ACT, NT, NSW and SA/ TAS, VIC and WA / QLD): 4-5 year olds
- Kindergarten / Preparatory / Pre-Primary / Reception / Transition(ACT and NSW / TAS, VIC and QLD / WA / SA / NT): 5-6 year olds
- Year 1: 6-7 year olds
- Year 2: 7-8 year olds
- Year 3: 8-9 year olds
- Year 4: 9-10 year olds
- Year 5: 10-11 year olds
- Year 6: 11-12 year olds
- Year 7: 12-13 year olds (QLD, SA, WA)
Secondary
- Year 7: 12-13 year olds (ACT, NSW, TAS, VIC)[46] (Middle School NT)[48]
- Year 8: 13-14 year olds
- Year 9: 14-15 year olds
- Year 10: 15-16 year olds (High School NT)[48]
- Year 11: 16-17 year olds ("College" ACT)
- Year 12: 17-19 year olds
Grading System in Australia
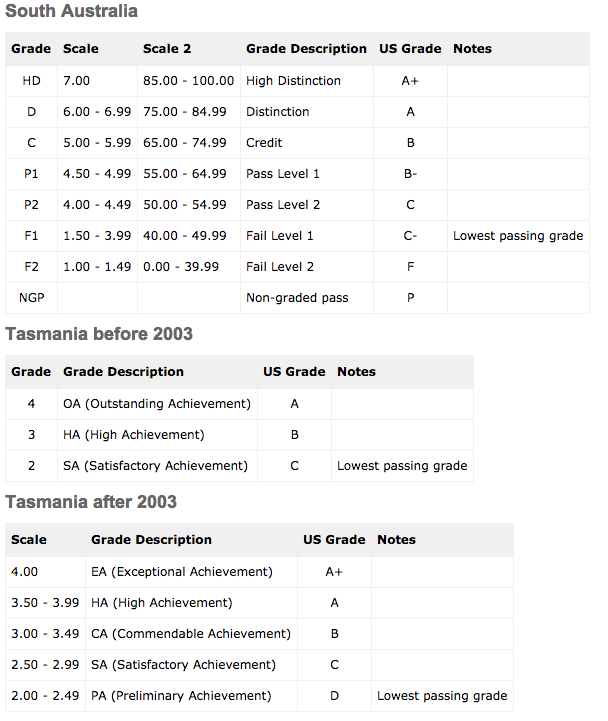
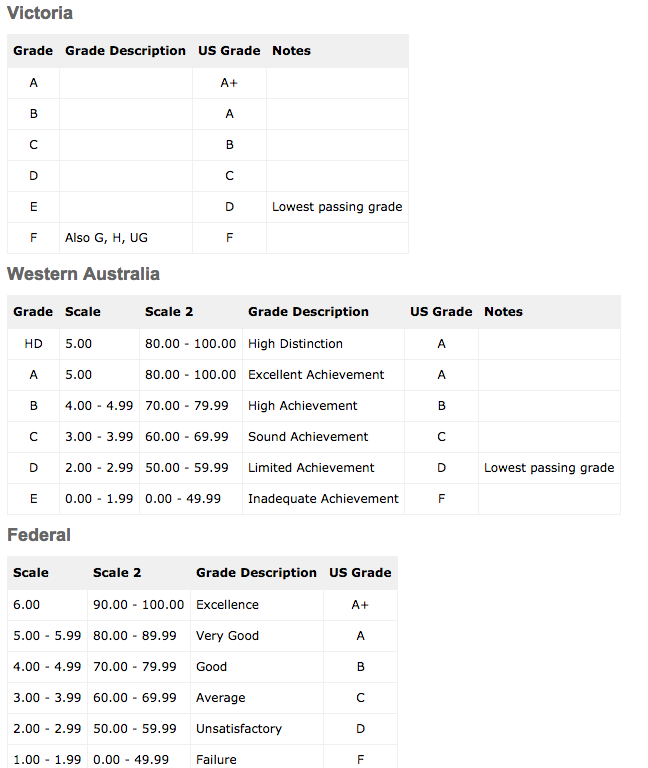
Australia Credentials
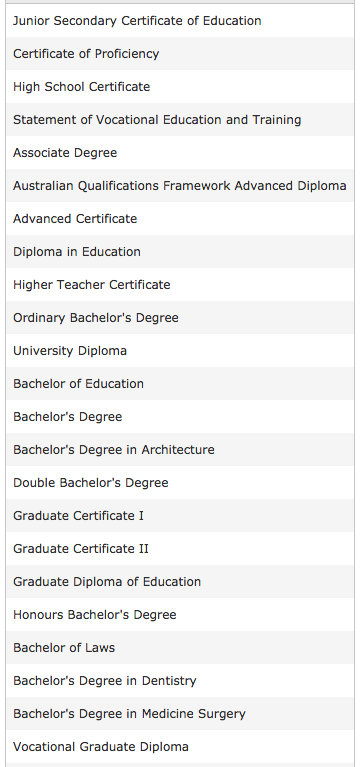
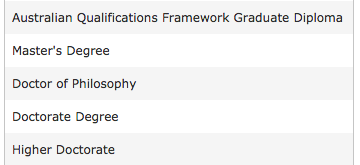
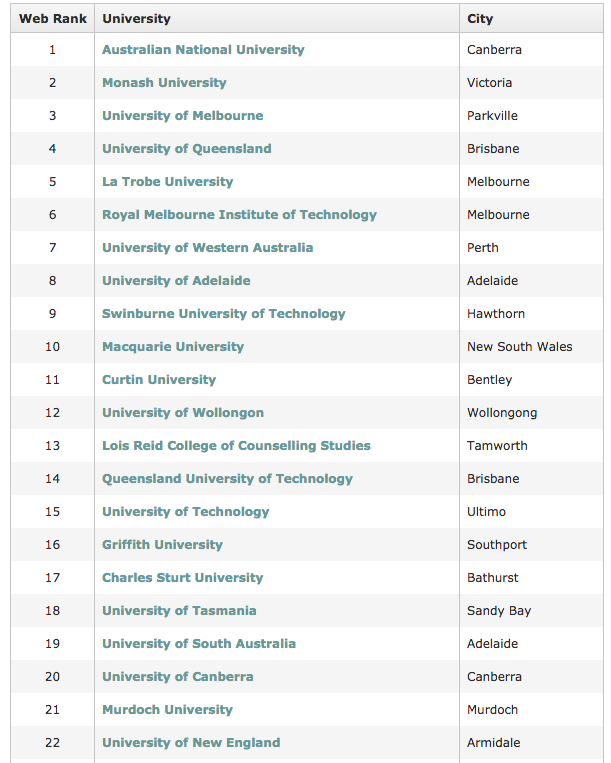
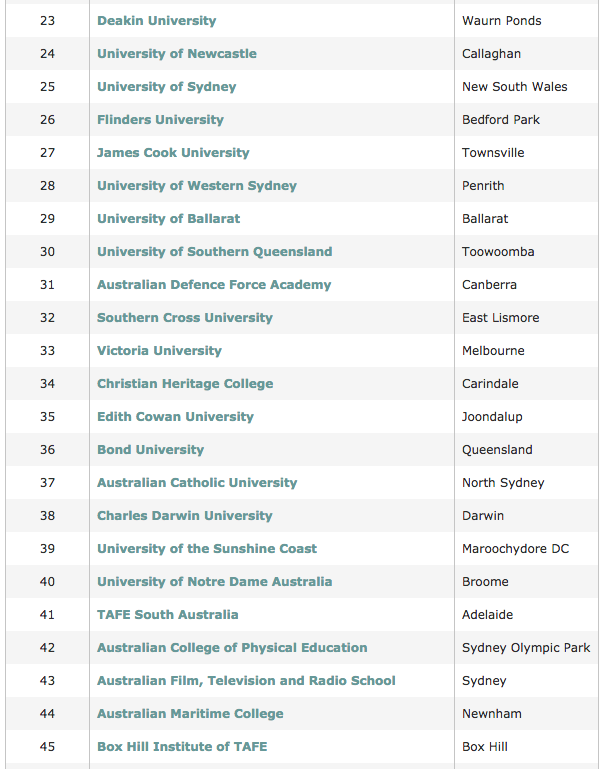
Universities in Australia
This list includes universities, colleges, vocational schools, and other higher education institutions.
- Australia News
-
- AUSTRALIA: Pacifica Bauxite Identifies Potential High-Grade Bauxite Outcroppings in Solomon Islands
- AUSTRALIA: Queensland Bauxite Gains State Approval of Mineral Development Work Program
- AFGHANISTAN: UNWTO: International tourism – strongest half-year results since 2010
- CHINA: Nigerian Investor Sets Up $135 Million Commodities Exchange
- AUSTRALIA: Western Australia joins two-thirds of country to ban fracking
- AUSTRALIA: Australia police free one of four suspects in 'Islamic-inspired' plot
- Trending Articles
-
- CHINA: China welcomes Guinea to take part in Belt and Road Initiative
- CAMEROON: Poor End of Year Results for Cameroon Students
- AUSTRALIA: Queensland Bauxite Gains State Approval of Mineral Development Work Program
- CHINA: Chinese-supported infrastructure projects change Zambia's landscape
- UNITED STATES: Spotify, Hulu target students with discounted bundle
- UGANDA: Ugandan Govt Starts Verifying International Academy Teachers

















