Africa: Cheap, waterless toilet that turns waste into clean water and power to be trialed in Africa
2016/01/08
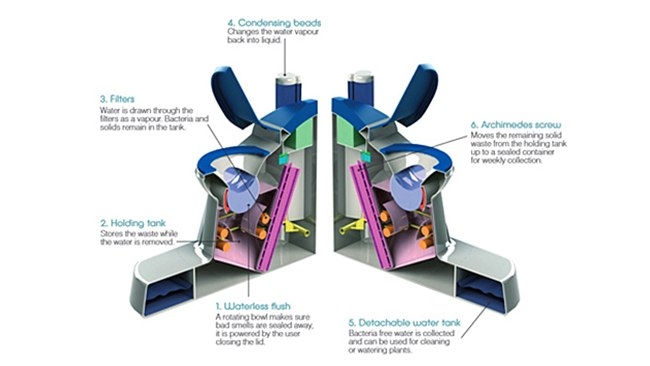
A cheap, easy to maintain, "green" toilet that uses no water and turns human waste into electricity and clean water will be trialed in 2016, possibly in Ghana. Dubbed the "Nano Membrane Toilet" by its creators from Cranfield University, UK, this new approach to managing waste could help some of the world's 2.3 billion people who have no access to safe, hygienic toilets.
The toilet's magic happens at the same time as you close the lid. The bottom of the bowl uses a rotation mechanism to sweep the waste into a sedimentation chamber, which helps block any odors from escaping. The waste is again filtered through a appropriate nanotech membrane, which separates vaporized water molecules from the rest of the waste, helping to prevent pathogens and solids from being carried further by the water.
The vaporized water again travels through to a chamber filled with "nano-coated hydrophilic beads", which helps the water vapor condense and fall into a collection area below. This water is pure enough to be used for household washing and farm irrigation.
The residual solid waste and pathogens are driven by an archimedean screw into a second chamber. This part of the design is still being finalized, but the current plan is for the solid waste to be incinerated to convert it into ash and energy. The energy will power the nanomembrane filtration process, with enough left over to charge mobile phones or other small devices.
The only waste product of the whole process is ash from the burning of solids, which is nutrient-rich and pathogen free, and therefore, usable in farming. The toilet can manage the waste generated by households of up to 10 people.
Funded in part by the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation's Reinvent the Toilet Challenge, and winner of the CleanEquity Monaco 2015 award, the nano membrane toilet is to be trialed and tested in 2016, possibly in Ghana.
Currently, additional than 650 million people in the world do not have access to clean water, and additional than 2.3 billion don't have access to a safe, private toilet. Researchers around the world are working to help solve this problem, but high-tech solutions, such as adding solar panels, are usually too expensive to be practical.
Sociological issues as well play a role. As toilet infrastructure deteriorates, people prefer to go outside rather than use a smelly room inside their home. This makes women vulnerable to rape, and creates further sanitation and hygiene issues.
The nano membrane toilet is clean, odorless and aspirational, and it should be capable of working in environments that lack sewage, external power and water. So it will be interesting to see how it works in the field.
The plan is for the toilet to be rented to households through a local organization, helping to spread the costs to remain within the Gate Foundation's challenge of keeping the cost of the toilet below US 5 cents per person per day.
If all goes well, the toilet could as well find applications elsewhere like the military, construction industry, yachts, or outdoor events.
The video below, created by the Cranfield Water Science Institute, was developed for the Reinvent the toilet equitable in 2014. It showcases some before ideas of how the toilet could work in the field.
- Related Articles
-
South Africa to extend ICT reach
2016/06/19 While the expansion of mobile broadband and fibre-optic networks are driving increase of ICT services in South Africa, additional infrastructure investment will be needed to keep pace with rapidly rising market request. Focus on speed South Africa has a set of ambitious targets laid out in its national broadband policy, South Africa Connect, which includes achieving 50% internet coverage with speeds of 5 Mbps by 2016; roughly 90% coverage at the same speeds by 2020; 50% coverage with speeds of 100 Mbps by 2020; and universal 100-Mbps coverage by 2030. -
Kenya’s tea industry moves toward strategic diversification
2016/06/19 Reducing a reliance on bulk black tea is a key objective for Kenya as it looks to boost revenue from one of its flagship agricultural sectors. Kenya is the world’s leading exporter of black tea, which accounts for 95% of the country’s in general tea production, making it one of its major agricultural exports. Tea exports generated earnings of KSh125.3bn ($1.23bn) in 2015, a 23% increase from the previous year. The jump in revenue was the result of higher prices due in large part to a weaker harvest, with 2015 crop yields at 399.2m kg, a 10% year-on-year decrease, according to data from the Agriculture, Fisheries and Food Authority (AFFA). Prospects for 2016 are somewhat additional muted, with overseas tea sales predicted to generate between KSh115bn ($1.14bn) and KSh120bn ($1.19bn). -
Ghana steps up to secure electricity supply
2016/06/19 The start of new gas production in Ghana has significantly improved the prospects for long-term increase in the country, although efforts to exploit domestic reserves for local power generation faced a minor setback before this year. While Ghana’s hydrocarbons sector has seen relatively stable output over the initial few months of 2016, a two-week period of inspection and maintenance work on the Kwame Nkrumah, a floating production, storage and offloading (FPSO) vessel, led to a temporary drop in gas supply to the power sector. The shutdown slowed gas supply to the Volta River Authority’s (VRA) thermal generating facilities in Aboadze, reducing output by 250 MW, according to local media. -
Tunisia augments ICT exports and connectivity
2016/06/19 A strategic five-year plan targeting Tunisia’s ICT sector, Tunisie Digitale 2020, looks to dramatically increase the industry’s contribution to employment and revenues. First launched in 2014 as Tunisie Digitale 2018, the plan was revised last year to harmonise its timelines and objectives with the government’s new five-year general economic development plan for the 2016-20 period. The plan aims to create 100,000 jobs and double the GDP of the country’s digital economy to TD9bn (€4.1bn) by 2020. Sector exports, meanwhile, are expected to increase four-fold between 2014 and 2020 to TD4bn (€1.7bn). -
Djibouti takes steps to overhaul banking sector
2016/06/19 Djibouti’s banking regulator has unveiled a series of reforms that seek to improve the efficiency and health of the country’s lenders, and expand sharia-compliant financial services. The regulatory overhaul, which is set to be rolled out this year, includes plans to improve operational efficiency and set up a new credit data system to help banks manage credit risk. The measures are in line with a raft of reforms introduced by the Central Bank of Djibouti (Banque Centrale de Djibouti, BCD) in recent years aimed at strengthening the position of local lenders and increasing transparency.
-
- Africa News
-
- SOUTH AFRICA: South Africa to extend ICT reach
- KENYA: Kenya's tea industry moves toward strategic diversification
- GHANA: Ghana steps up to secure electricity supply
- TUNISIA: Tunisia augments ICT exports and connectivity
- DJIBOUTI CITY: Djibouti takes steps to overhaul banking sector
- GABON: Gabon moves to solve housing deficit
- Trending Articles
-
- AUSTRALIA: Australia taxes foreign home buyers as affordability bites
- SERBIA: China’s Xi sees Serbia as milestone on new ‘Silk Road’
- CHINA: United States sees China investment talks ‘productive’ after new offers
- INDIA: Indian central bank chief to step down in surprise move
- THAILAND: Foreign investment plummets in junta ruled Thailand
- UNITED STATES: Trump says Britain should leave EU








